10 Reasons Why Consumers Choose to Eat Vegan Food
Written by Johanna van Langen
Published 24 July 2024
The popularity of vegan food continues to grow worldwide as consumers embrace various reasons to eat more plant-based. Understanding these motivations is essential for marketers to optimise their strategy and connect with their audience.
This blog post provides insights into the rational and emotional reasons why consumers choose to eat vegan food. Continue reading to learn how health benefits, animal welfare, sustainability, social influences, and other factors drive your customers’ vegan food choices.

Easily calculate the positive impact of your vegan business initiatives
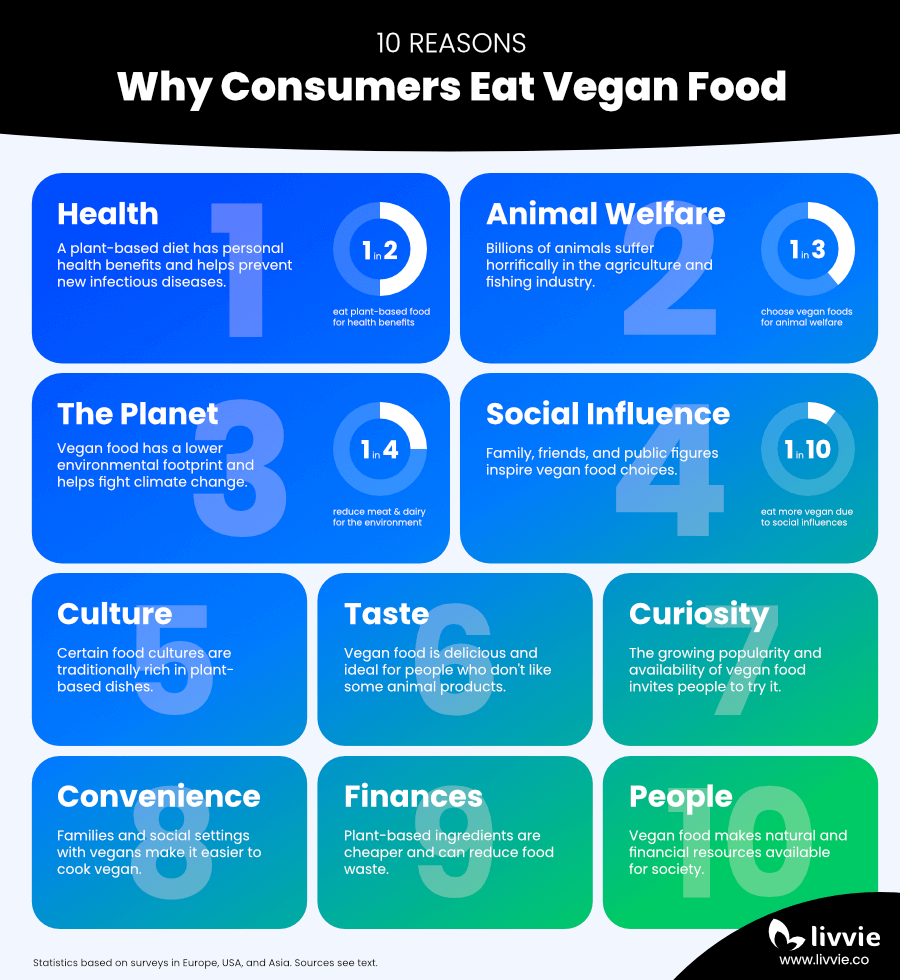
1. Personal and Population Health Benefits of Plant-Based Food
2. Animal Welfare is a Key Motivator to Eat Vegan
3. Vegan Food as Part of a Sustainable Diet
4. Social Influence on Vegan Food Choices
5. Cultural Background Shapes Dietary Habits
6. Taste Preferences Drive Food Choices
7. Curiosity to Try Vegan Food
8. Cooking Vegan Can Be Convenient
1. Personal and Population Health Benefits of Plant-Based Food
Individual and population health benefits are a primary driver for consumers who choose plant-based food over animal products.
Plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and several types of cancer. These diets can also improve the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and manage autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. About half of the consumers in USA, Asia, and Europe cite personal health benefits as a main reason to eat more vegan food.
Around 10% of people have a food allergy, and 68% of the global population is lactose intolerant. These consumers choose vegan food to avoid allergens and physical symptoms from intolerances.
Another reason people eat plant-based is the risk of new infectious diseases and pandemics created by animal agriculture. Habitat destruction to clear land for feed drives wildlife into rural areas, increasing the risk of transmitting infectious diseases to humans. Animals in livestock and fish farms live in unhealthy conditions and are treated with antimicrobials to prevent disease. This use of antimicrobials can cause microbes to evolve in resistant strains that can pass to humans as zoonotic diseases. Europeans indicated concerns about antibiotics (15%) and zoonoses (9%) as motivations to reduce meat and dairy consumption.
The growing awareness on these benefits for their own health and society are inspiring consumers to choose vegan food more often.
2. Animal Welfare is a Key Motivator to Eat Vegan
Concern about animal welfare is the second key motivator for consumers to choose vegan food over meat or dairy. For many people who adopt an entirely vegan lifestyle, animal welfare is the most important reason.
Every year, our food system claims the lives of 83 billion land animals and 1,5 trillion fish. The horrific conditions these animals endure under standard industry practices are regularly exposed to the public. People naturally care about animals, and many have them as companions. The realisation that farm animals think and feel like dogs and cats motivates consumers to no longer support the suffering caused by animal agriculture.
The compassion for animals inspires consumers to make ethical food choices that align with their values, driving the demand for vegan products. Around one-third of consumers in the USA, Asia, and Europe choose plant-based food over meat and dairy for animal welfare reasons.
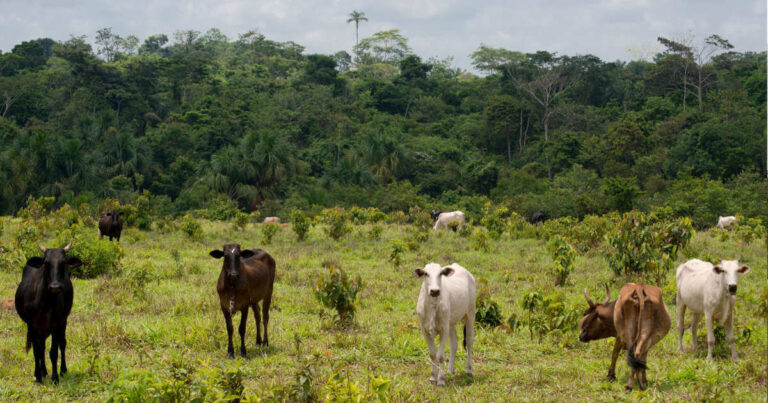
3. Vegan Food as Part of a Sustainable Diet
The third major reason people prefer to eat vegan food is to reduce their environmental footprint. Our current food system has a heavy impact on the planet, primarily due to livestock farming. Climate change is a growing public concern as floods, heatwaves, and droughts, become more frequent and severe.
Despite producing only 18% of the world’s calories, animal agriculture emits the majority of greenhouse gases from our food system. Livestock farming requires substantial amounts of feed and claims most of our agricultural land for growing crops and grazing pastures. This intensive land use makes meat and dairy production the main drivers of deforestation and wildlife habitat destruction.
Additionally, animal agriculture has a high water footprint and pollutes natural resources with manure, fertiliser, pesticides, and medicinal residues. These practices harm ecosystems and contribute to the degradation of our natural environment.
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental cost of livestock farming and feel responsible for making sustainable food choices. A quarter of consumers name environmental concerns as a principal motivation to eat more plant-based. By emphasising how vegan food choices contribute to a healthier planet, you can appeal to eco-conscious customers.

4. Social Influence on Vegan Food Choices
Consumer decisions are constantly influenced by their social environment, including friends, family, and social media. Over the past few years, the number of people adopting a vegan, vegetarian, or flexitarian diet has risen markedly, particularly among Millennials and Gen Z. Almost everyone now has a friend or family member who is vegan or vegetarian.
Seeing loved ones embrace vegan food and discussing the values that motivate them can influence one’s perception and choices. Practical situations that expose omnivores to vegan food also play a role. For instance, when dining with a vegan, people are more likely to cook vegan dishes or choose a restaurant with vegan options on the menu.
Social influence is especially powerful for families where parents need to prepare nutritious meals for everyone. If one family member is vegan, it is often more convenient to cook plant-based for the whole family.
Nowadays, social media amplifies the influence of veganism. Veganism has claimed a strong online presence, with many influencers, athletes, and celebrities advocating for a vegan lifestyle. They use their social platforms to share their dietary choices and the reasons behind them, inspiring millions of followers.
Endorsements from loved ones, friends, and public figures help to make plant-based food choices the social norm. Of European consumers, 10% indicate that their social environment is a key motivational driver to eat more vegan food.
5. Cultural Background Shapes Dietary Habits
Cultural background is one of the most influential factors that define what you like to cook and eat. While Western cuisines are very dependent on meat and dairy, many other food cultures embrace plant-based diets.
East-Asian cuisines are partly shaped by Hinduism and Buddhism, which forbid violence against animals. As a result, these cuisines are rich in plant-based proteins like tofu, and traditional Indian food is predominantly vegetarian or vegan.
Middle Eastern cuisines have developed with strict rules around the halal and kosher use of animal ingredients. The distinction between animal and plant-based ingredients has led to the creation of plenty inherently vegan dishes.
Ethiopian and Eritrean cuisines are largely plant-based due to the Orthodox-Christian tradition of fasting, during which people abstain from all animal products.
Latin American foods are traditionally rich in plant protein from beans and legumes. Caribbean cuisine is influenced by the Rastafarian movement and the Jamaican Ital food culture, based on respect for nature and all living beings.
Consumers with certain cultural backgrounds may be more likely to choose vegan food due to culinary familiarity or religious belief. Offering vegan food options is therefore particularly important if you want to ensure an inclusive experience for diverse groups of customers.

6. Taste Preferences Drive Food Choices
Taste preference is another reason for people to choose plant-based food. While the decision to adopt a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle is often driven by deeper values, taste remains crucial in daily food choices.
Many flavourful foods are inherently plant-based and veganised dishes can be as satisfying as their animal-based counterparts. Meat and dairy alternatives can also be delicious in their own right, leading even omnivores to enjoy vegan food regularly.
There are also omnivores who simply don’t like certain animal ingredients such as meat, fish, butter, or cheese. For these consumers, taste can be a strong motivator to choose plant-based alternatives or order vegan dishes.
By appealing to taste in food descriptions and marketing communications, you can invite a broad audience to choose vegan dishes.
7. Curiosity to Try Vegan Food
The rising popularity of vegan food has increased its visibility, triggering curiosity among many to try it. Knowing others who eat plant-based or share positive feedback about vegan products or recipes can encourage people to experiment with vegan food. Seeing plant-based options on the menu at their favourite restaurant may also spark an interest to try a vegan dish.
Curiosity isn’t limited to momentary food choices. Hearing friends and celebrities promote the benefits of a vegan diet can inspire them to try it for a certain period. A notable example is Veganuary, a popular challenge encouraging people to adopt a vegan diet during January.
This curiosity to discover new foods contributes to the growing number of people embracing vegan food.

8. Cooking Vegan Can Be Convenient
Choosing plant-based food can be convenient for consumers, whether in the moment or by adopting a vegan lifestyle. If one person in a household is vegan, cooking one plant-based dish for everyone is more convenient than preparing multiple meals. This simplicity may be a strong reason to eat vegan, especially at home.
In social settings, when one or several people in a group are vegan, it can be easier to cook entirely plant-based for a dinner party or select a restaurant with many vegan options. This ensures that everyone can enjoy the meal without restrictions.
Moreover, animal products like meat, fish, and dairy tend to expire quickly, whereas plant-based ingredients often have a longer shelf life. This makes plant-based cooking not only convenient but also practical for reducing food waste.
The convenience of cooking plant-based makes it attractive for some consumers, simplifying meal preparation and ensuring inclusivity.
9. Economic Benefits of Plant-Based Ingredients
Financial benefits are another interesting reason for consumers to choose vegan food. Because of the inefficiency of livestock farming, animal products are fundamentally expensive. Although many governments offset the high intrinsic cost of animal products with subsidies, prices remain high.
Plant-based foods are often more affordable, especially when cooking with raw ingredients instead of ready-made alternatives. Plant-based foods also tend to have a longer shelf life than animal products, reducing food waste and saving money.
Even when eating plant-based meat and dairy alternatives, a vegan diet can still be cheaper than an animal-based diet. By optimising your pricing strategy, you can attract price-sensitive consumers to buy vegan foods.

10. Choosing Vegan in Solidarity With People
Many benefits of plant-based food impact society and consumers may choose to eat vegan out of solidarity towards other people.
Reducing meat and dairy consumption conserves natural resources such as land and water. This makes them available to feed billions of people who face food insecurity and water shortages. Eating plant-based also protects public health by helping prevent new zoonotic diseases and future pandemics.
Some consumers prefer sustainable foods to leave a viable planet for future generations and support disadvantaged people. Environmental destruction for animal agriculture and climate change impact low-income nations disproportionately. Native lands are often repurposed for cattle grazing or to grow feed crops for export to wealthier countries. This disrupts local food supplies and affects the resilience of nature and Indigenous cultures.
Conditions in the animal industry are dire not just for animals but also for employees. Besides physical injuries, slaughterhouse workers often suffer from mental health issues due to the horrific animal suffering they witness.
The impact of animal agriculture on the environment and public health carries a massive economic burden. Additionally, Western governments spend around 20% of their budgets on animal agriculture subsidies. Redirecting these funds to education, healthcare, or welfare is a strong social reason to choose more plant-based foods.
Consumers Have Various Reasons for Choosing Vegan Food
People have several good reasons for adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet or eating plant-based food regularly. Health benefits, animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and social influence are some of the most powerful drivers. Most consumers are motivated by a combination of reasons to choose vegan food.
Understanding these motivations is key to creating effective marketing strategies that attract new customers, connect with your target audience, and increase vegan food sales.
See how your vegan business initiative addresses customer motivations with the Livvie food impact calculator.

Help others understand why consumers choose vegan food by sharing this article.

