Reduce Land Use With a Vegan Diet to Protect the Planet
Written by Johanna van Langen
Published 24 October 2024
Reducing land use is essential for protecting the environment and ensuring a sustainable and fair food supply for future generations. The high demand for land in our current food system has severely disrupted natural ecosystems, particularly driven by animal agriculture.
By adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet, you can substantially decrease the amount of land needed for agriculture, leading to numerous environmental and societal benefits. In this article, you’ll discover why choosing plant-based food lowers land use and helps protect ecosystems, fight climate change, and ensure global food security.

Calculate how much land you save with your diet
Why Vegetarian and Vegan Diets Use Less Land
Adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet is one of the most impactful ways to lower your environmental footprint by reducing the land needed for food production. Livestock farming demands vast amounts of land with devastating consequences for ecosystems and the climate. Plant-based foods require significantly less land, making them a more sustainable option. By choosing to eat vegetarian or vegan, you can save a substantial amount of land and help to protect our planet and food supply.
How Much Land Do We Use for Food Production?
The global population has grown rapidly from 1 billion people in the 18th century to 8 billion today, partly enabled by agricultural intensification since the Industrial Revolution. With projections estimating a population of 10 billion by 2050, we rely on land as a finite resource to house and feed everyone. Of Earth’s total surface, only 29% is land, and just 71% of that is habitable and suitable for agriculture, with the rest consisting of glaciers, deserts and other barren areas.
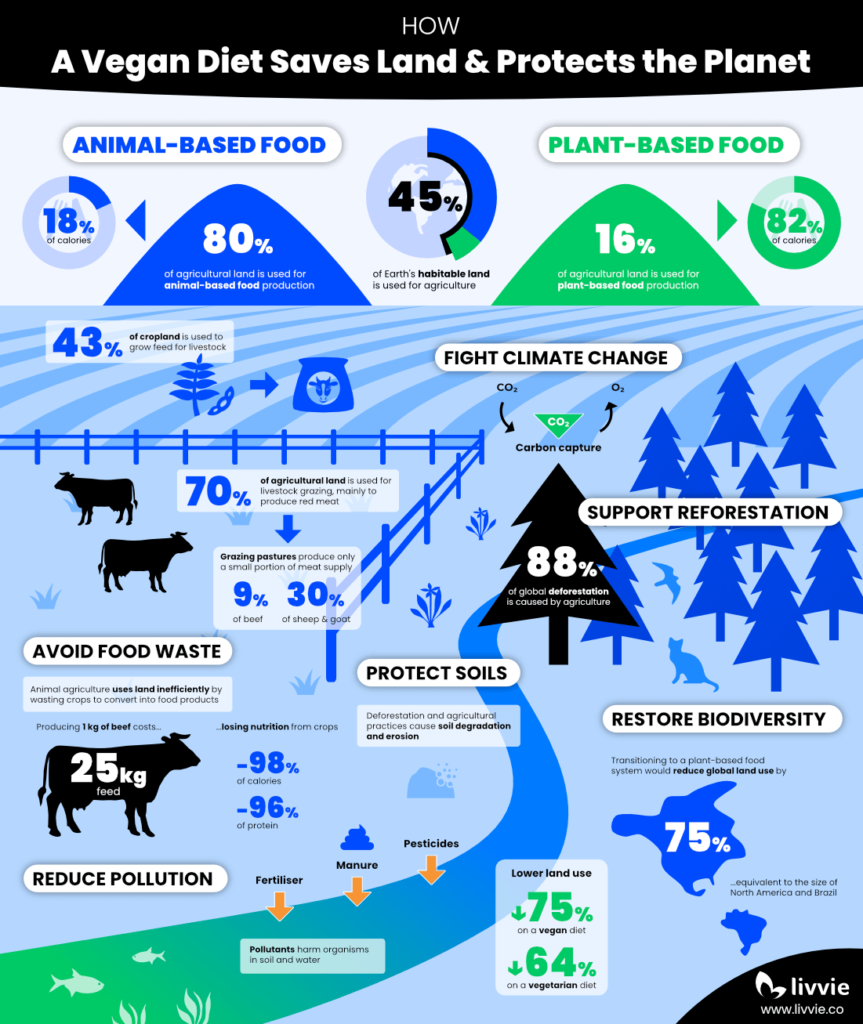
Half of Earth’s habitable land is already used for agriculture, whereas only 1% is occupied by housing and infrastructure. A staggering 80% of agricultural land is dedicated to livestock farming as grazing pastures and cropland for feed, while only 16% of land is used to grow crops for direct human consumption. This excessive need for land to produce animal-based products is the underlying reason for their high environmental footprint, contributing to climate change and threatening our food supply.
The Inefficiency of Animal Agriculture
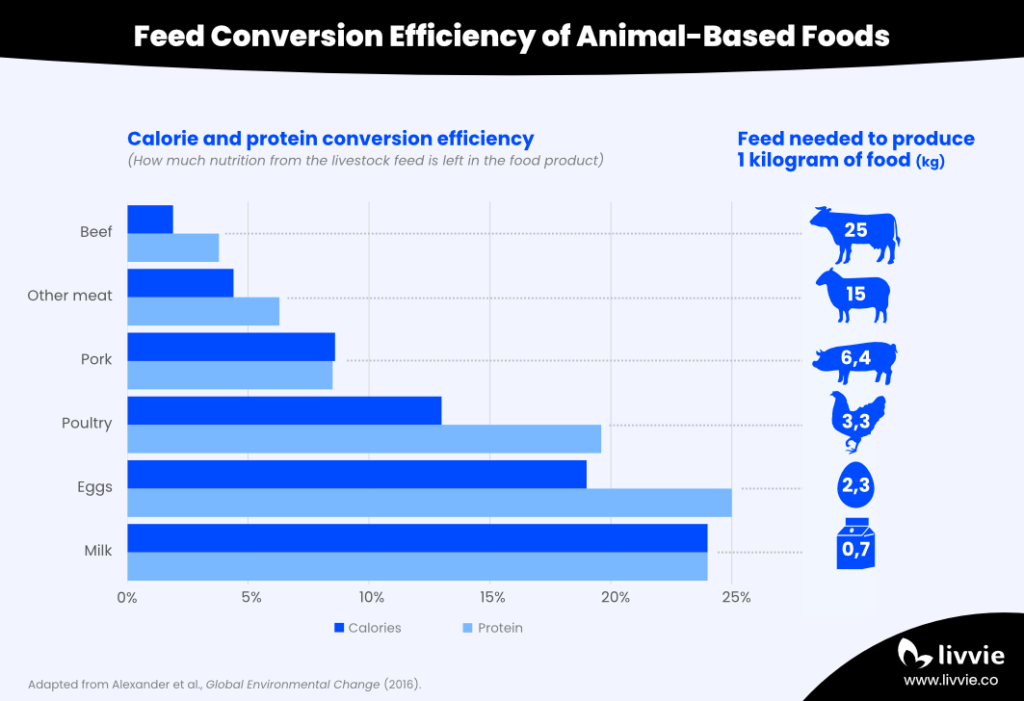
Livestock farming claims most agricultural land due to the high demand for grazing pastures and feed crops, but provides only 18% of the world’s calorie supply. This imbalance illustrates the inefficiency of animal agriculture which is the result of energy loss from converting plants into animal-based foods.
Farm animals consume large quantities of grass or crops like soy and corn and use most of their nutritional energy to stay alive. Only a small percentage of calories and protein is converted into edible products like meat or dairy. That is why it takes, for example, 25 kilograms of feed to produce just 1 kilogram of beef. This inefficiency is the main reason why so much land is used to feed livestock rather than humans.
By eating plant-based, you eliminate the need for intermediary energy loss, as you consume crops directly, wasting less food and land.
Land use for feed crops
The inefficiency of animal agriculture becomes very evident when considering how much land is used to grow crops for livestock instead of humans. Approximately 43% of global cropland is dedicated to producing animal feed. If more people switched to vegetarian or vegan diets, this land could be repurposed to grow food directly for human consumption or returned to nature.
Land use for grazing pastures
In addition to cropland, vast areas of land are used for livestock grazing, which demands even more land than crop-feeding. Around 70% of agricultural land is used for grazing animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, yet these animals provide only 9% of global beef and 30% of sheep and goat meat. This excessive need for grazing land is a major driver of deforestation, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss, particularly in tropical regions where natural ecosystems are destroyed for pasture.

How Much Land You Save With a Vegetarian or Vegan Diet
Switching to a vegetarian or vegan diet can drastically reduce your land use footprint. Plant-based proteins like legumes, grains, and soy require much less land to grow compared to meat, dairy, or eggs. For example, it takes up to 100 times less land to produce wheat or tofu than beef.
A vegetarian diet reduces land use by 64%, while a vegan diet lowers your land use by 75%, helping to protect our food supply, preserve ecosystems, and mitigate climate change. Most of this impact is already accomplished by simply ditching red meat and dairy. If everyone adopted a plant-based diet, we could reduce global land use by 75%, an area equivalent to the size of North America and Brazil combined. By freeing up land previously used for animal agriculture, we enable recovery of biodiversity, support carbon capture through reforestation, and ensure a healthier planet for future generations.
How Lower Land Use Helps the Environment and Society
Reducing land use is crucial for protecting the environment and ensuring a sustainable and equitable food supply for future generations. The high demand for land of our food system and agricultural practices have disrupted natural ecosystems in several ways. By adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet, you can substantially reduce the demand for agricultural land, leading to a various environmental and societal benefits by protecting ecosystems and food security.
1. Avoid Deforestation
Deforestation is one of the biggest environmental issues of our time, largely driven by animal agriculture. Forests are vital ecosystems that support a rich diversity of plant and animal species, regulate the water cycle, and capture carbon dioxide. Unfortunately, one-third of Earth’s forest cover has already been destroyed, and we continue to lose 5 million hectares each year. Agricultural expansion is responsible for 88% of deforestation globally, primarily to clear land for grazing pastures and feed crops such as soy.
Tropical rainforests are especially affected by the global demand for meat and dairy, contributing to carbon dioxide emissions and the loss of biodiversity. By choosing a vegetarian or vegan diet, you reduce the for need for agricultural land, preventing further deforestation and enabling reforestation. This protects both the trees that act as carbon sinks as well as the wildlife that depends on them for survival.
2. Prevent Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining balanced ecosystems, which in turn provide humans with resources such as clean air, water, and fertile soil. However, agricultural expansion has led to the loss of natural habitats for countless species and continues to threaten 86% of the world’s endangered species.
Particularly livestock farming takes up a disproportionate amount of land, replacing wildlife habitats with monocultures or grazing pastures that drastically reduce biodiversity. Tropical rainforests, home to much of the world’s biodiversity, are especially affected by animal agriculture. By reducing the demand for land through eating more plant-based, natural habitats can be restored, helping to prevent species extinction and support ecosystem resilience.
3. Mitigate Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most urgent challenges for our planet and society, and our food system is a major contributor. Clearing natural vegetation such as forests to make room for cropland or grazing pastures releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Deforestation alone accounts for 12% of global greenhouse gas emissions, primarily driven by animal agriculture. Additionally, livestock emit methane, and fertiliser used to grow crops emits nitrous oxide, highly potent greenhouse gases that further exacerbate climate change.
Shifting towards a plant-based diet reduces the need for deforestation and lowers the emissions associated with animal farming. With a vegetarian or vegan diet, you lower your carbon footprint by reducing emissions and preserving forests that capture carbon, mitigating climate change.
4. Decrease Soil Degradation
Healthy soils are critical for growing food, regulating water supplies, and supporting biodiversity. However, modern agricultural practices cause soil degradation, compromising land fertility and resilience against floods and droughts. Overgrazing, monoculture farming, and excessive use of fertiliser and pesticides have reduced soil quality and contributed to erosion and desertification.
Animal agriculture is a major contributor to soil degradation because of the large areas of land required for both grazing and feed production. By transitioning to a vegetarian or vegan diet and supporting sustainable agriculture, you allow soils to regenerate and maintain their fertility to protect the environment and food supply for future generations.

5. Reduce Environmental Pollution
Animal agriculture is also a leading source of environmental pollution. Fertiliser and pesticides used in crop production, combined with runoff from animal waste, contaminate ecosystems and water resources. Nutrients from fertiliser and manure leach into rivers, lakes, and oceans, leading to eutrophication, a process that depletes oxygen levels in water, causing “dead zones” where aquatic species can’t survive.
Pesticides used on cropland and chemicals from livestock farming further pollute soils and waterways, endangering biodiversity and potentially contaminating freshwater supplies for human use. By adopting a plant-based diet, you can help reduce the demand for land and minimise environmental pollution caused by animal agriculture.
6. Protect Food Security
With the global population expected to reach 10 billion by 2050, ensuring food security is becoming an urgent challenge. Animal agriculture is an inefficient way to produce food, wasting massive amounts of crops and therefore land to yield relatively few nutrients. For instance, converting crops into beef results in the loss of 98% of calories and 96% of protein.
By eating plant-based foods such as legumes, grains, and vegetables, you consume crops directly and avoid the waste associated with raising animals for food. By adopting a vegetarian or vegan diet, you support a more efficient food system and help to alleviate global hunger.
Lower Land Use of a Vegan Diet Protects the Planet
Switching to a vegetarian or vegan diet is one of the most effective ways to reduce your environmental footprint, primarily by reducing the demand for agricultural land. By choosing plant-based foods, you avoid the inefficiencies and resource waste associated with animal agriculture. This simple dietary change helps prevent deforestation, protect biodiversity, fight climate change, reduce soil degradation and pollution, and ensure a more secure global food supply.
Your dietary choices can make a real difference by saving land and helping to restore ecosystems, creating a more sustainable food system and future. Track how much land you save with your daily food choices by downloading the Livvie diet impact calculator.
Share this article to motivate others to eat plant-based more often and save land.
Track Your Impact
Inspire your vegetarian or vegan food choices by calculating your impact on 22 parameters.